Transformer winding – wind your own transformer at home using some simple mathematics, and also known which size of copper I want to use when winding the Transformer.
want to what is transformer?
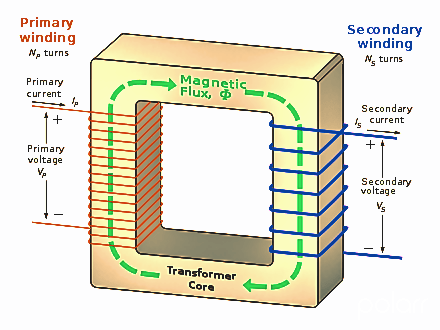
The transformer is defined as an electrical device that works in the principle of the electromagnetic force. The transformer contains copper wire and metallic sheets. there is a different type of transformers are available in the market. Mainly that transformers are using to convert the high voltage into low volt or convert the low voltage into high volt.
That’s commonly known as step-up transformer and step down transformer. Step up transformer does the job of converting the low voltage into a high voltage level. And the step-down transformer that does the job of converting the high voltage into low voltage.
The transformer contains the primary and the secondary coil windings. In step down transformer, the primary coil contains less number of turns and the secondary coil have least more of turns than the primary. In a step-up transformer, the primary coil is thick copper wire with less number of turns. And the secondary coil having more numbers of turns.
Types of transformer commonly using an electronic device
There are different type of transformer are using. The commonly using transformers are
- Step up transformers
- Step down transformers
- Air core transformers
- Iron core transformers
- Toroidal transformers
In this article, I am going to simply say about how to calculate the transformer winding and which size of the copper wire we need to choose while winding the transformer.
Transformer winding coil turns calculation
The winding of the transformer is based on the equation of
NS/NP = VS/VP
NS = Number of turns in secondary coil
NP = number of turns in primary coil.
VS = voltage in secondary coil.
VP = voltage in primary coil.
For the demonstration on purpose, I am going to construct a 12-volt transformer that working in a 230 volt. Now we need to calculate the number of turns in the primary and secondary coil of the best Transformer.
I am not mentioning the core size it will be changing according to the power of the transformer. This equation is only for calculating the number of turns during the transformer winding.
VS = 230 volt. VP = 12 volt.
NS = ? NP = 80 turns.
How we want to calculate the secondary turns of this transformer.
NS/ Np = VS/ VP
NS = ( VS*NP) / VP
= ( 230/1500) *12
=1533.33 turns
That is 1540 turns needed for producing 12 volt on primary coil.
Copper wire gauge and Amper
You are confused when winding a transformer, is which gauge of the copper wire I used for the winding transformer. And
how many amperes can we get? Or you are decided to make a 5 a transformer and you don’t know which copper I use?
Here is the solution for theses confusion. Choose the copper size according to the specific amper you need.
Copper gauge amp rating
| Gauge number (awg) | Ampere |
| 7 | 44.2 amp |
| 8 | 33.3 amp |
| 9 | 26.5 amp |
| 10 | 21.2 amp |
| 11 | 16.6 amp |
| 12 | 13.5 amp |
| 13 | 10.5 amp |
| 14 | 8.3 amp |
| 15 | 6.6 amp |
| 16 | 5.2amp |
| 17 | 4.1 amp |
| 18 | 3.2amp |
| 19 | 2.6 amp |
| 20 | 2.0 amp |
| 21 | 1.6 amp |
| 22 | 1.2 amp |
| 23 | 1.0 amp |
| 24 | 0.8 amp |
| 25 | 0.6 amp |
| 26 | 0.5 amp |
| 27 | 0.4 amp |
| 28 | 0.3 amp |
| 29 | 0.29 amp |
| 30 | 0.22amp |
To make 5 amp transformer use 16 gauge copper wire on the transformer when winding.
Also check, Pir motion sensor relay on/off circuit
Automatic lead acid automatic battery charger circuit with pcb



Please mention the working time of this chart.
Looks like you are mixing primary and secondary 😉
Not mixing if you mixed it will not work
How did you get 1533 from the equation (230/1500)*12?
Where did you get 80 turns on the given above VS=220, NS=12, NS=?,NP=80.
I am confused.
What is 1500? Use this equation vs/vp=ns/np
Celý výpočet je niak nejasný. Podla čoho ste udali tie číslá ked ste nevypočítali najprv prierez jadra E trafa. Potom sa može počítat Primár a sekundár. A aj nato je koeficient 45 a podla toho sa počítá počet závytov na 220 na sekundár.
výpočty sú správne môj priateľ pozorne skontrolujte obsah
What is the best formula then
Thank you
You are welcome
Your method is very old..why you not use uH.
No mention where The 80 came from? NP/NS = VP/ VS
230 primary volts ÷ 12 secondary volts= 19.16 so how many turns is a mystery from these calculations.
Thanks for the information. The windings calculation is not
Correct however.
According to my calculations you are correct. I have looked up calculations and Double checkit! Nice call!
That’s for your comments
okay but how to assume the number of turns in the primary coil
Your calculation on the winding and number of turn and voltage is very very wrong… Please study the calculation well.. Thank you..
Above is wrong, very wrong.
NS/NP = VS/VP
NS = ( VS*NP) / VP = (12*80)/230 = 4.2 turns
as 80 turns on primary is very small, I think you meant if 80 turns on the secondary how many on the primary
NS/NP = VS/VP
NS = (VS*NP)/VP
NS*VP=VS*NP
(NS*VP)/VS=NP
NP=(80*230)/12 = 1533 turns
how many milimetre are 27gauge and 15gauge?