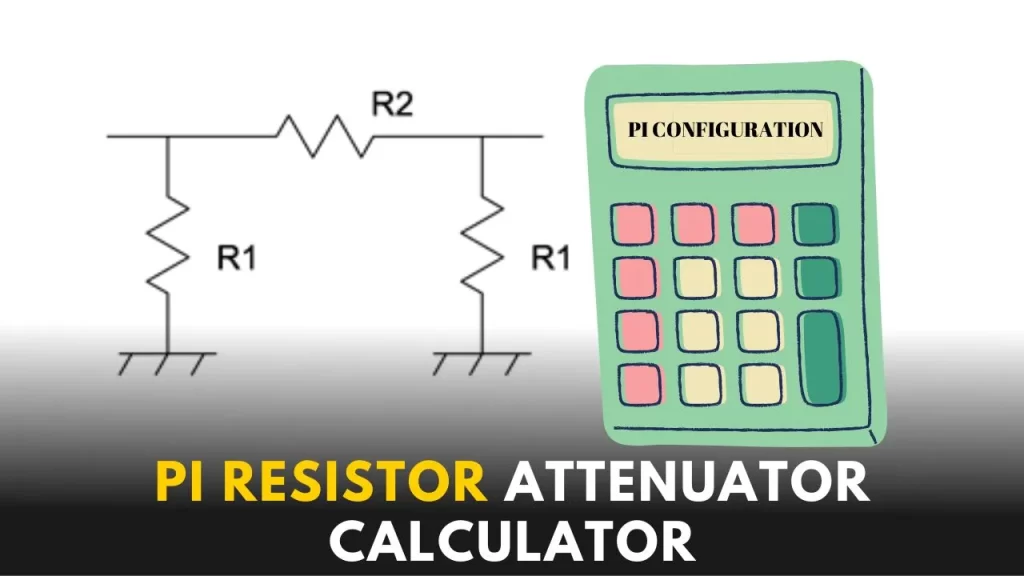
The Pi resistor attenuator is a circuit that uses a combination of resistors to reduce the amplitude of a signal without introducing significant distortion. The circuit is similar to a voltage divider, but is designed to handle larger signals and to minimize distortion.
Pi Resistor Attenuator Calculator
Attenuation (A): dB
It is a passive circuit, meaning it doesn’t require any external power source to operate. The circuit is made up of a combination of fixed value resistors, usually in a T or a Pi configuration, that are used to divide the input voltage and reduce the amplitude of the signal.
The purpose of an attenuator is to reduce the amplitude of a high-level signal to a lower level without introducing significant distortion. This can be done to prevent the overloading of an input stage of an amplifier, or to match the output level of a signal source to the input level of a circuit.
Resistor Attenuators are commonly used in a wide range of applications such as
- Radio frequency (RF) and microwave communications: They are used to match the output of a signal source to the input of a receiver or amplifier.
- Audio: They are used to reduce the level of a high-level signal before it is input into a preamp or mixing console.
- Measurement: They are used to reduce the level of a high-level signal before it is input into a measurement device such as an oscilloscope or spectrum analyzer.
- Power amplifiers: They are used to reduce the level of a signal before it is input into a power amplifier to avoid distortion and damage.
In Overall, the resistor attenuator is a passive circuit that uses a combination of resistors to reduce the amplitude of a signal without introducing significant distortion. It is widely used in a variety of electronic systems to match the output level of a signal source to the input level of a circuit or to prevent overloading of an input stage of an amplifier