The Zener Diodes are a special type of diode that can used as a Voltage regulator with the help of a few components. So in this Article, I’m explaining the details of how the Zener diode is used as a voltage regulator and how it works.
First of all, we need to know what is diodes, zener diodes, and how it is working. This is very important to know before going to the Main topic. So more understanding I’m explaining with diodes. What are diodes? How do these diodes work in a DC or AC?
What is a diode in electronics?
A diode is an electronic component that will allow the passage of current in only one direction. The most common diode uses a p-n junction. In other words, the p-n junction diode is one of the simple semiconductor devices that will conduct the current through the p-n junctions.
The p-n junction diodes are used as rectifiers and reverse voltage blockers in numerous electronic circuits. Why the p-n junction is also called a junction diode? The p-n junction allows the large current flow through the forward bias and it will be highly resistant to the reverse bias. so there is a little complication in understanding.
Don’t worry using an image representation I can clarify the doubts about the p-n junction, Reverse bias, and also the forward bias. From the name itself, you can understand the reverse bias and forward bias terms. let’s look at the below image to understand the terms in an easy way.
Pn junction diode
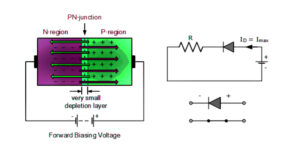
If we are making the electrical connections in both ends of N-type and P-type material ( Because of the diode built with p and n-type semiconductor material ). The P region is connected to the battery-positive terminal, and the N junction is connected to the battery-negative terminal.
During this connection, the free electrons can cross the depletion region from one side to the other side. This behavior of the pn junction with the depletion layer as a potential barrier produces an asymmetric current conducting a two-terminal electronic component is Known as a PN junction.
So with the help of the image, you can understand now. what about the forward bias and reverse bias, zero bias? now it is the time to explain more deeply about the bias of diodes.
Zero bias
In zero bias condition, there is no external voltage potential applying in the PN junctions of the diode. so it is clear that the potential difference between the two ends of the diode is zero then it is called the zero bias condition of a diode.
Reverse bias
The reverse bias, from the name reverse, represents the reverse polarity connection of the diode. Yes, the potential difference is applied to the diode in reverse directions. the positive terminal of the battery is connecting to the N junction of the diode and The negative connection of the battery will connect to the P junction of the diode.
So there is a big depletion layer is there in between the pn junction. the electrons will not pass through this depletion layer so there is no current passage through the diode is occurs.
Forward bias
From the name forward bias, it is clear that the connections will be the forwarded type. This means that the P junction is connecting to the positive terminal of the battery and the N junction is connecting to the negative terminal of the battery. the work is already discussed above paragraph so I’m not explaining more about the forward biasing.
For the above explanations about diode and its working reverse biasing, forward biasing is clear now I understand that you know about how normal pn junction diodes work in various electronic equipment. now we are going to the zener diode section.
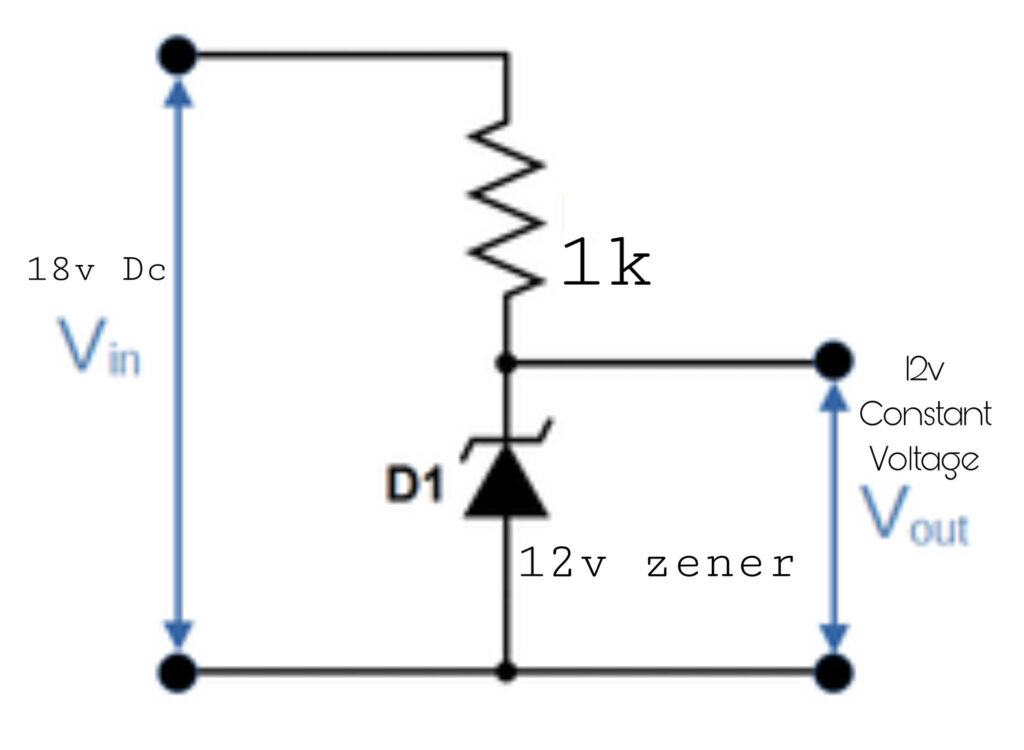
Discussing zener diode workings and also about zener voltage regulator circuit diagrams. A diode can regulate the input voltage? it can deliver a constant potential difference?
What is Zener diode
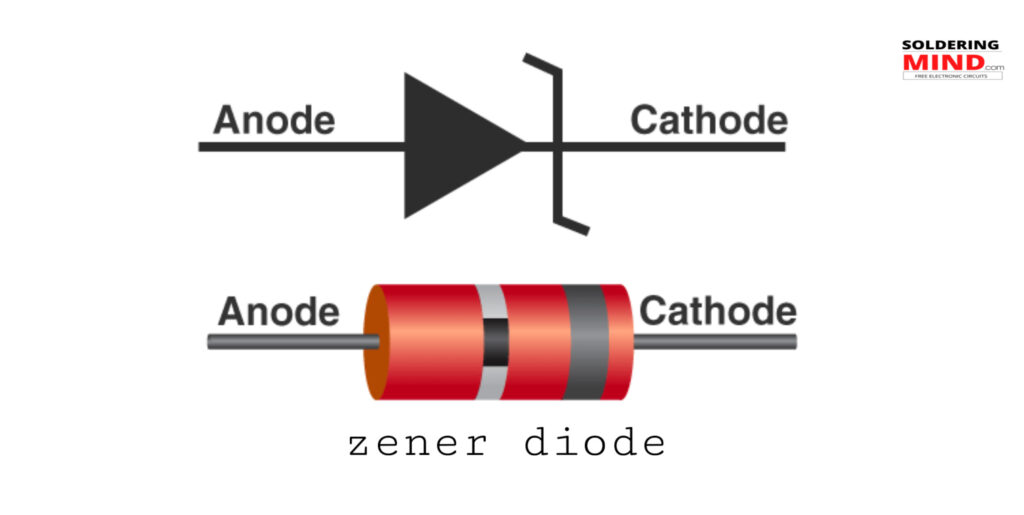
The zener diode is also a tiny semiconductor diode. which will conduct the current through it but with some conditions are there. The normal diodes work in forward bias conditions but the zener diodes will work in the reverse bias with a rated critical potential difference.
The zener diodes do not allow the current flow from the anode terminal to the cathode, in the reverse bias reaching the rated zener voltage. for example, the Zener diodes are available in the market with 3,3v, 5.1v, 6.2v, 10v, 11v, etc. These are the turn-on voltage of the Zener diode.
Zener diode explanation
The zener diode is also known as the reverse direction diode or breakdown diode. The diode is a heavily doped semiconductor. This electronic component is designed for working in reverse bias conditions with special rated voltage.
Why is the Zener diode used as a voltage regulator?
The zener diodes are used as voltage regulators because the voltage drop across the diode is constant. The supply voltage needs to be high, above the zener diode voltage the diode start to conduct. The zener diode connected to any device in parallel the voltage output will be constant.
What is the Zener voltage of a Zener diode
The breakdown voltage is the special characteristic of the zener diode. So every single zener diode is rated its breakdown voltage in their data-sheet. The zener diode connects in the circuit and at that time a constant voltage is developing in the circuit this is known as Zener Voltage.
If the voltage exceeds and the point of zener conducts the current in that point is known as the breakdown voltage of that zener diode.
Application of Zener diode
The zener diode is used as a voltage regulator. The main thing is the voltage drop in the diode is constant. so we can implement this zener diode in op-amp volt by comparing the voltage ranges in many situations.
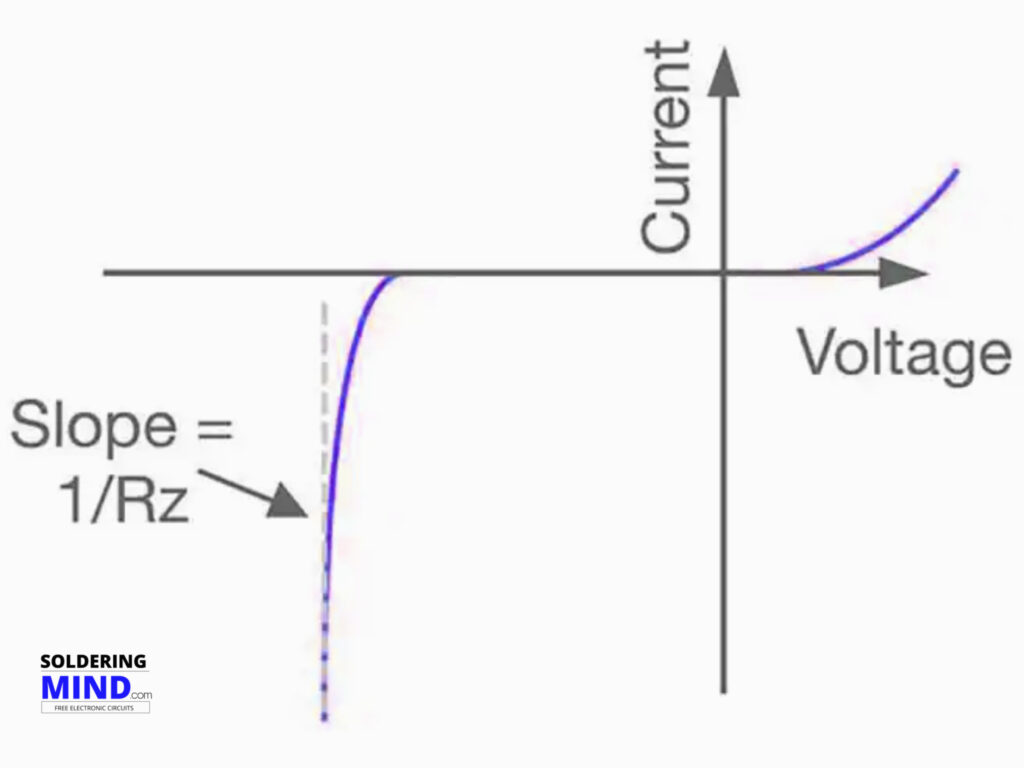
Also, we can implement led circuits to protect the high input voltage spikes. The diode connecting parallel with any components will get the same voltage range ( constant potential difference ).